For high-net-worth individuals, entrepreneurs, and family businesses in Bengaluru, understanding the nuances of Indian succession law is critical to safeguarding your legacy. From ancestral properties in Indiranagar and Koramangala to tech startups in Whitefield, this guide demystifies the legal frameworks—Hindu, Christian, Parsi, and Muslim—governing adoption, guardianship, marriage, and inheritance.
1. Foundations of Hindu Succession Law
1.1 Sources & Scholarship
- Vedas & Shrutis: The bedrock of dharma and family duties.
- Smritis (Manusmriti): Early codification of inheritance norms.
- Commentaries (Nibandhas): Evolving interpretations that inform modern courts, including the Karnataka High Court’s landmark judgments on coparcenary rights.
1.2 Legislative Milestones
- Hindu Succession Act, 1956 & 2005 Amendment: Equal coparcenary rights for daughters—vital for Bengaluru families holding ancestral bungalows in Basavanagudi.
2. Adoption & Guardianship: Securing Minor Heirs
2.1 Hindu Adoption & Maintenance Act, 1956
- Key Requisites: Capacity of adopter (including marital consent), capacity of giver (natural or court guardian), and adoptee eligibility (under 18, Hindu, unmarried).
- Example: The Reddy family of Jayanagar adopted a child, ensuring he inherits shares in their IT firm via a valid court-sanctioned process.
2.2 Guardianship under Karnataka Courts
- Natural Guardians: Father and mother, recognized by Bangalore’s Family Courts.
- Powers & Limits: Guardians must seek Karnataka High Court or Magistrate approval for property transactions exceeding one year.
3. Marriage & Succession: Hindu Marriage Act, 1955
3.1 Validity & Succession Impact
- Conditions: Monogamy, consent, degrees of prohibited relationships, sapinda links (up to 3 generations maternal, 5 paternal).
- Local Insight: Registration at the Bengaluru Sub-Registrar adds enforceability—crucial for spousal succession rights.
3.2 Marital Remedies
- Judicial Separation & Maintenance: Bangalore courts award maintenance under Section 24—directly affecting spousal shares in estate.
4. Christian, Parsi & Muslim Succession
- Indian Succession Act, 1925: Christians and Parsis enjoy testamentary freedom—used by prominent Bengaluru banker families to structure their wills.
- Muslim Personal Law: Quranic shares apply; only 1/3 of assets freely willed. Tech entrepreneur Mr. Khan used this flexibility to endow 1/3 of his startup’s ESOP to charity.
5. Hindu Succession Act (HSA), 1956
5.1 Coparcenary Rights
- 2005 Amendment: Daughters in Malleswaram acquire equal rights in ancestral property.
- Court Precedent: Karnataka HC clarified daughters’ shares in Mysore palace-linked estates.
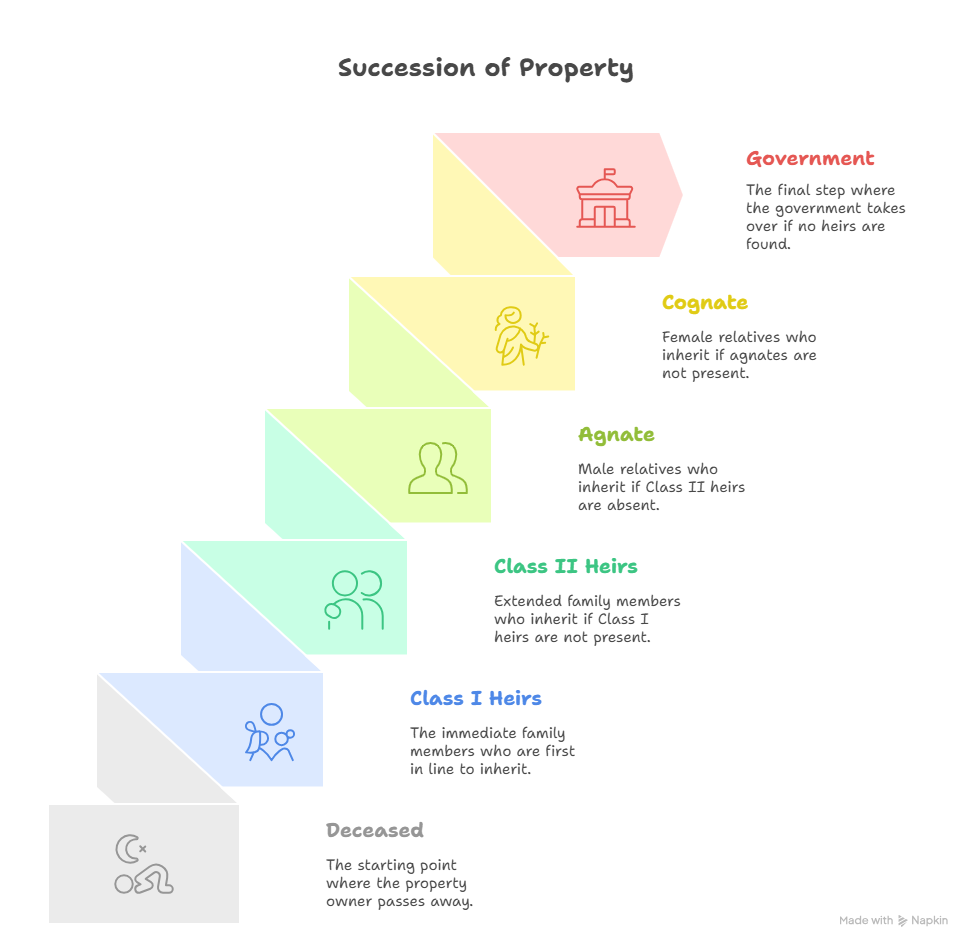
5.2 Intestate Succession (Sections 8–13)
- Class I Heirs: Equal shares for spouse, children, and mother.
- Class II & Beyond: Father, siblings, agnates, and cognates—decision hierarchy applied in Bangalore estate disputes.
5.3 Succession of Females (Sections 14–16)
- Absolute Ownership: Female Hindu’s property devolves to children, husband, and parents—reflected in recent Bangalore probate rulings.
6. Intestate Succession Flowchart for Estates
7. Bengaluru Case Study: The Sharma Estates of Basavanagudi
Mr. and Mrs. Sharma held both ancestral land in Basavanagudi and a growing spa business in Koramangala. Upon Mr. Sharma’s sudden demise:
- Adoption & Guardian mechanisms ensured their minor grandson’s maintenance.
- Coparcenary Amendment empowered their daughter to share equally in ancestral property—avoiding family rifts.
- Estate Plan + Trust funded via life insurance ensured seamless business continuity without probate delays in City Civil Court.
8. Practical Takeaways for Bengaluru’s Elite
- Adoption & Guardianship Documentation: Obtain court orders from Bangalore Family Court.
- Marriage Registration: File at local Sub-Registrar to secure spousal and children’s rights.
- Wills & Trusts: Consider revocable/discretionary trusts for your Whitefield startup shares.
- Partition Agreements: Use at offices like Richmond Town to clarify ancestral asset splits.
- Periodic Reviews: Post life events or Karnataka state amendments (e.g., Property Tax changes).
9. Next Steps: Your Bangalore Succession Strategy
Partner with advisors experienced in the estate planning landscape to craft a legally robust, tax-efficient succession plan.
Mobile: +91 97436 83444 | Email: sandeep@sandeepnsetty | Discuss over coffee!

